What are immersive technologies?
Immersive technology transforms the digital experience by bringing together the virtual with users’ sight, sound and event touch. Ranging from virtual reality and augmented reality to haptics, immersive technologies are new ways of creating, displaying and interacting with applications, content and experiences.
Immersive technologies allow a person to feel part of an artificial, simulated environment – for example, immersive theatre requires the audience to interact with the set, props and actors, while an immersive air control dashboard may allow the operator to see and interact with real-time monitoring data.
Virtual reality
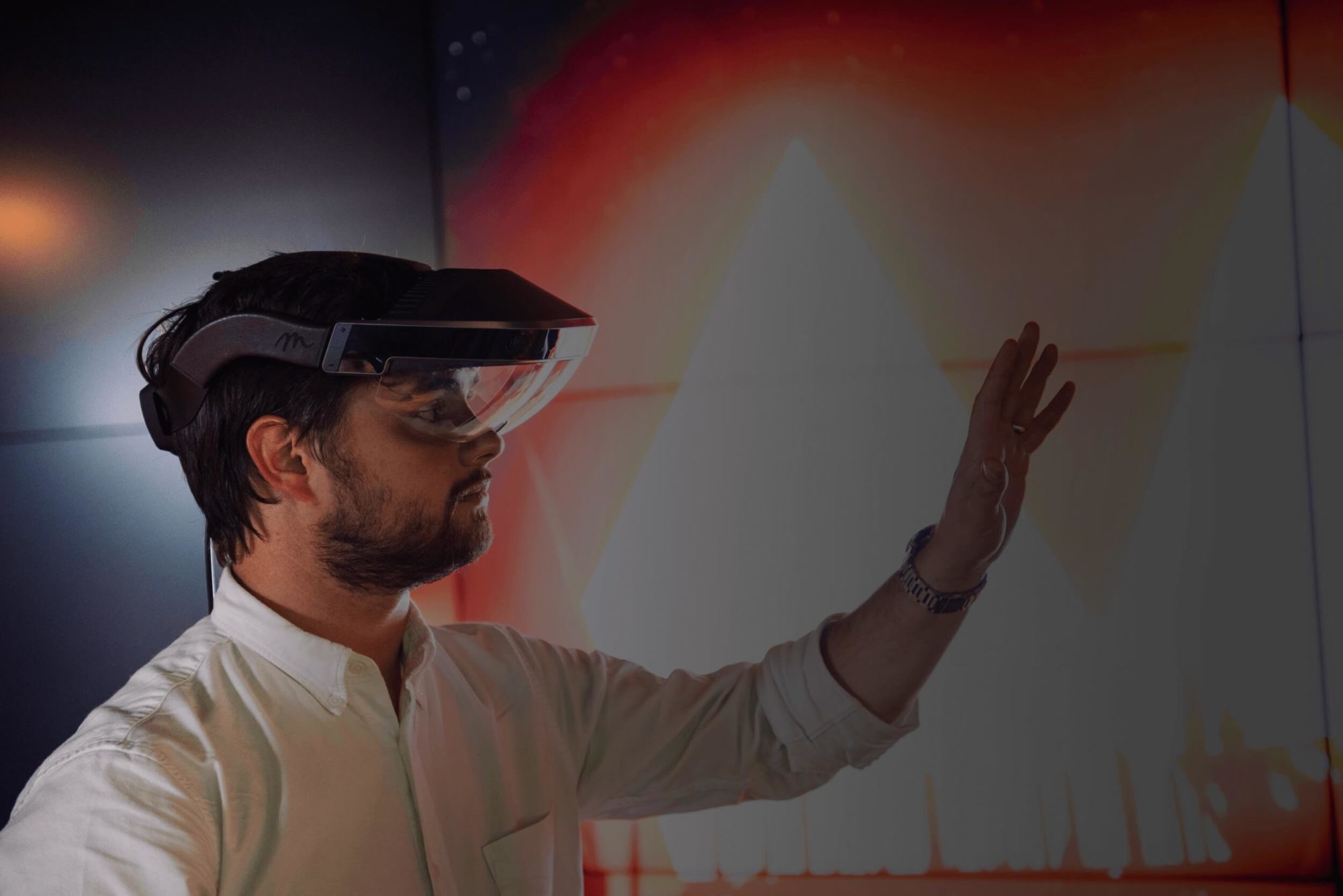
Virtual reality (VR) completely replaces a user’s surroundings with a digital environment using a head-mounted display (HMD) with two near-eye displays, one for each eye. This is a closed and fully immersive 3D environment. VR lends itself to both industrial applications and creative experiences with new modes of storytelling. Perhaps the most widely known immersive technology, virtual reality has been around since the 1990s but it’s only in the past decade that VR has become an increasingly large part of our professional and private lives, running a spectrum of use cases from employee training to creative outstanding immersive entertainment experiences.
Augmented Reality
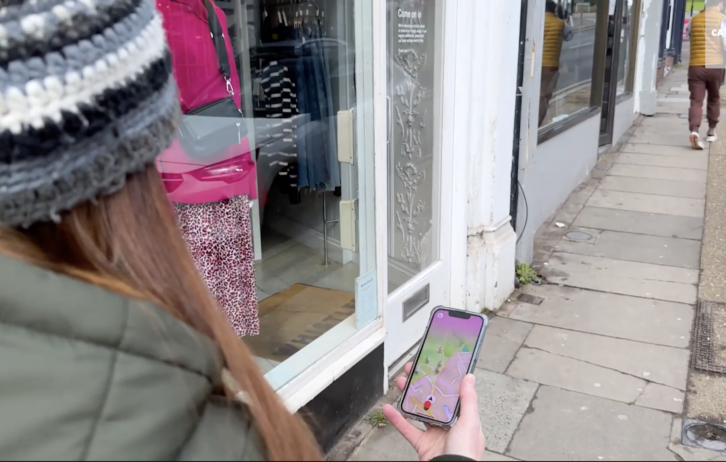
Augmented reality (AR) creates an immersive experience for users by blending the real with the virtual. Utilising computer vision and machine learning algorithms the device can understand the ‘real world’ in both a spatial and semantic sense. AR seamlessly blends the digital and physical worlds by allowing a user to overlay digital objects in a physical space. Digital Catapult has helped cultural institutions reach new audiences with AR and helped retail brands explore new AR-powered solutions to grow, and innovate within, their business. Most recently, Digital Catapult teamed up with Niantic, Cartoon Network, Studio Wayne McGregor and three UK immersive studios to develop augmented reality-powered consumer experiences.
Haptics
Haptic technologies are commonly referred to as ‘3D touch’ or ‘kinaesthetic interaction’. Unlike other immersive technologies, haptics uses tactile feedback including pressure, vibrations, and movements to enable the user to “feel” whilst in a virtual environment, increasing the levels of interaction to cover multiple senses. Haptic tech is likely to be one of the main ways for users to interact with applications and content in future computing paradigms, whether that’s spatial computing or in the “metaverse”. In 2020, Digital Catapult mapped the UK haptic ecosystem to uncover future use cases, players and opportunities – read the report here.
The rapid pace of development of immersive technologies has created many new opportunities for businesses to solve problems, seize new opportunities, and push innovation forward.
Why immersive experiences or solutions?
The 2022 Immersive Economy report from Immerse UK estimated the UK immersive economy had a turnover of £1.4 billion, a significant contributor to the UK economy, with other 2,000 immersive companies operating around the country. In many industries, immersive tech offers new ways of interacting, analysing, and creating content. Here are a few examples of why immersive experiences and technologies have been applied to existing cross-industry problems.
- Training
- Product design and prototyping
- Online and offline retail
- Content creation
Training
From the defence sector to energy, from healthcare to sports, immersive technologies have transformed the way training can be designed and delivered. The use of VR and AR has increased the speed and quality of training, and allows a more hands-on training experience which is very valuable and usually difficult to achieve in conventional classroom settings. This includes soft skills as well as technical ones, for example handling difficult situations or managing a team, and research shows that employees who undergo training in VR retain the information almost four times better than via training methods. Digital Catapult cohort alumnus MOONHUB has worked with companies such as Just Eat and the Royal Opera House to deliver VR training.