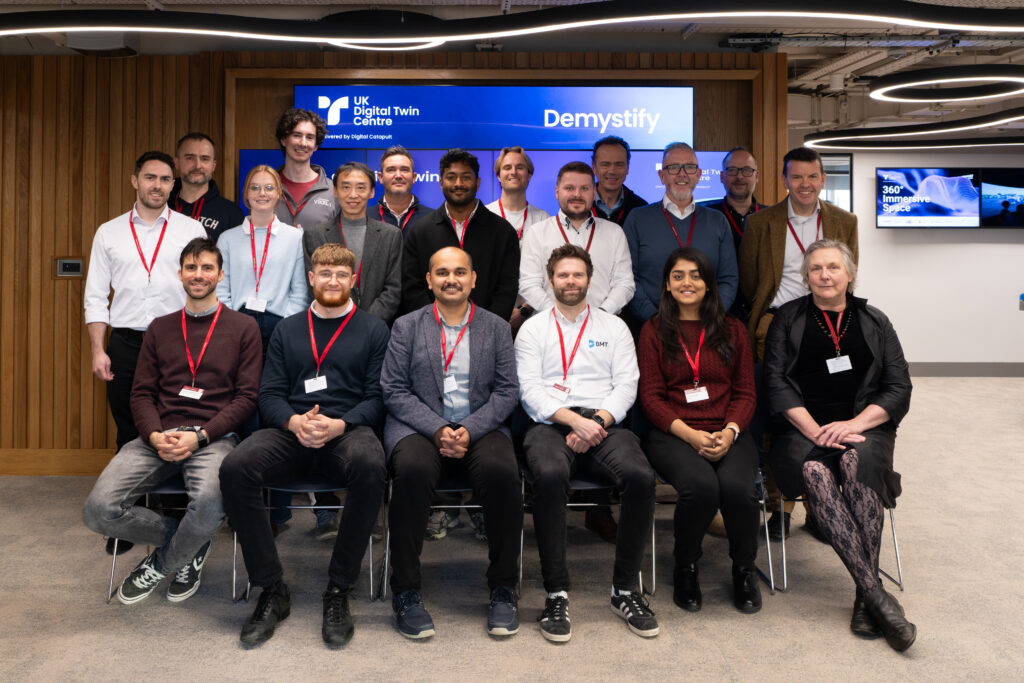
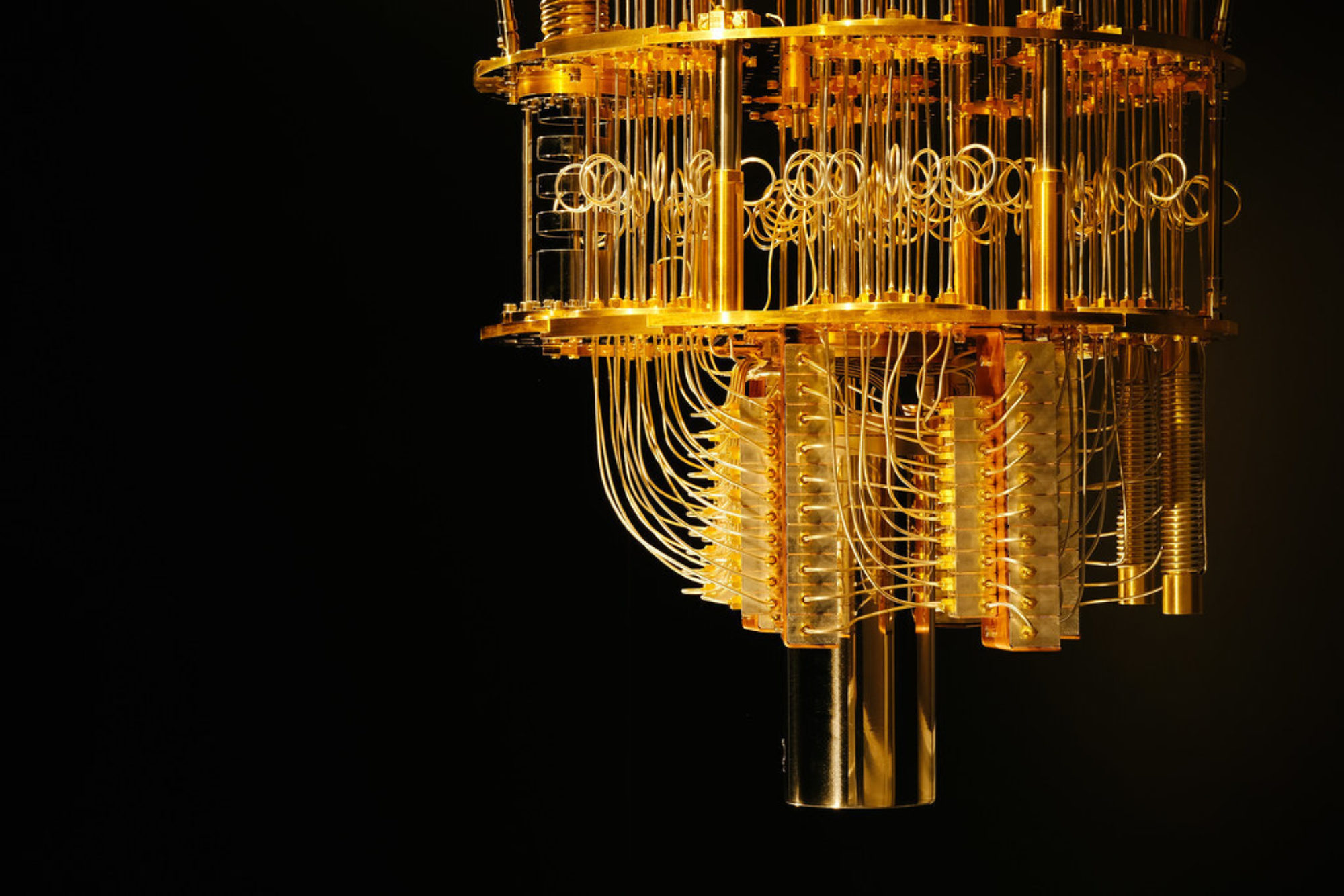
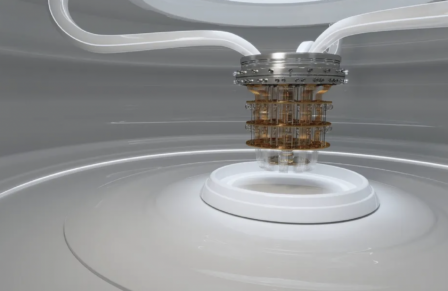
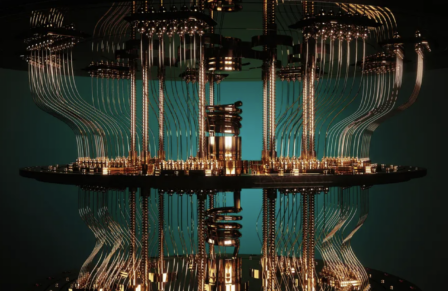
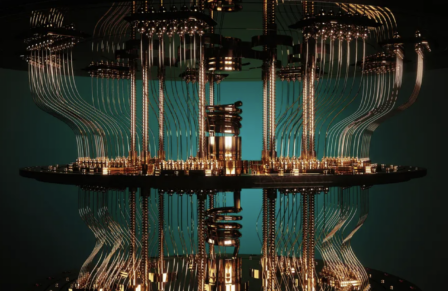
Quantum computers depend on quantum effects that are only relevant at small scales. A qubit, the quantum equivalent of a bit, can be in a “quantum superposition” of two different states at the same time. Compared to normal or “classical” computing, where a bit is only ever in one of two binary states, a qubit can hold much more information due to this superposition of states.
A quantum computer, parallel processing over many qubits, can give huge benefits over classical computers for some computations problems.
For example, finding a room temperature superconductor would help solve the world’s energy problems, but classical computers can’t simulate the required quantum systems with many entangled particles. Medical research could benefit because classical computers can’t simulate large molecules. Machine learning algorithms are also sometimes limited by classical computing constraints. In the future all these difficult problems will be solved by quantum computers, leveraging their fundamentally different computing approach.
We are working with our industrial partners to separate the opportunities from the hype, and understand the specific problems that may be best solved on quantum computers in the near future. We help organisations become “quantum ready” to reap the benefits of quantum computing, with future use cases possibly including optimisation, simulation of physical systems and machine learning. We are working to develop a blueprint for a quantum/classical hybrid data centre with experts in classical data centres, networking, quantum computing and quantum communications.